- Products
- DevSecOps
- DevSecOps Platform
Comprehensive application security products for every phase of the software development lifecycle
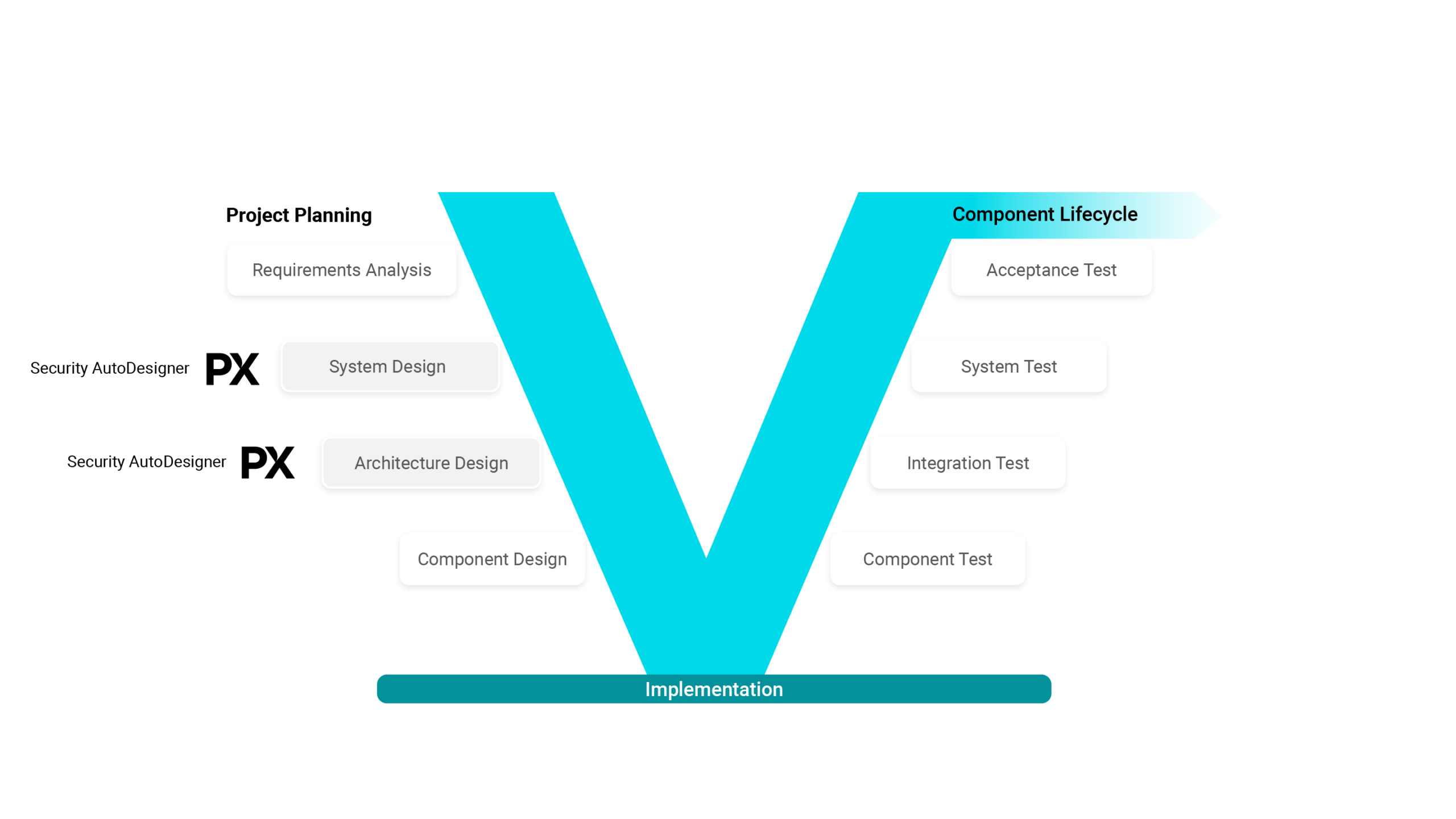
- Security AutoDesigner
Automatic vehicle & ECU threat analysis & risk assessment (TARA)
- Code Security Manager
Secure development with source code generated SBOM
- SW Supply Chain Security
Scan for known vulnerabilities with binary generated SBOM
- Security AutoTester
Reveal zero-day software vulnerabilities with automated fuzz testing
- DevSecOps Platform
- Vehicle Protection
- Fleet Protection
- Theft Prevention
- DevSecOps
- Services
- Resources
- Blog
- Company